Are you a poultry farmer looking to keep your chicken flock healthy and disease-free? In this article, we will explore the best practices for preventing diseases in a chicken flock. From maintaining good hygiene and biosecurity measures to implementing proper vaccination protocols, we will provide you with valuable insights on how to protect your chickens from common diseases. So grab a pen and paper, because by the end of this article, you will be armed with the knowledge to keep your feathered friends happy and healthy.
Biosecurity Measures
Quarantine New Birds
One of the best practices for preventing diseases in a chicken flock is to quarantine new birds. When introducing new birds into your flock, it is important to isolate them for a period of time to ensure they are healthy and free from any potential diseases. This allows you to monitor them closely and prevent the spread of any contagious infections. During the quarantine period, you should observe the new birds for any signs of illness or abnormal behavior, and keep them separate from the rest of the flock.
Control Visitor Access
Controlling visitor access is another important biosecurity measure to prevent diseases in your chicken flock. Limiting the number of people who have contact with your birds reduces the risk of introducing new pathogens into your flock. Visitors, especially those who also have poultry, can unknowingly carry diseases on their shoes, clothing, or hands. It is essential to have strict protocols in place to ensure that all visitors follow proper biosecurity measures, such as wearing clean clothing and footwear, and practicing good hand hygiene before entering the chicken coop or handling the birds.
Implement Cleaning and Disinfection Protocols
Maintaining a clean and hygienic environment is crucial for preventing diseases in a chicken flock. Implementing regular cleaning and disinfection protocols will help reduce the risk of pathogen transmission. Clean and disinfect all areas where the birds reside, including the coop, nesting boxes, feeders, and waterers. Use disinfectants that are specifically designed for poultry use and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper application. Cleaning and disinfecting not only removes any potential disease-causing organisms but also helps eliminate pests and parasites that can negatively impact the birds’ health.
Proper Waste Management
Proper waste management is essential for maintaining a healthy chicken flock. Effective waste management practices include regularly removing and disposing of manure, properly storing and disposing of dead birds, and providing clean bedding materials. Accumulated manure can harbor various pathogens and attract pests, increasing the risk of disease transmission. Removing manure from the coop and surrounding areas on a regular basis not only reduces the risk of diseases but also improves air quality and overall flock health.
Vaccinations
Regular Vaccination Schedule
Vaccinations are an important aspect of disease prevention in chicken flocks. Following a regular vaccination schedule recommended by a veterinarian ensures that your birds are protected against common diseases. Different vaccines may be required depending on the region, flock type, and prevalent diseases. Vaccinations help build immunity in the birds, making them less susceptible to infections. It is crucial to administer vaccines according to the recommended dosage and timing to ensure optimal protection. Keep a record of the vaccinations given to each bird to track their immunization status effectively.
Consulting a Veterinarian
To establish an effective vaccination plan and ensure the overall health of your chicken flock, it is advisable to consult a veterinarian. A veterinarian with poultry expertise can assess your flock’s specific needs and recommend appropriate vaccinations based on regional disease risks and your flock’s health history. Regular check-ups with a veterinarian can help detect any potential health issues and address them before they become severe. The veterinarian can also provide guidance on disease prevention, biosecurity measures, nutrition, and overall flock management practices.
Nutrition and Hydration
Balanced Feed
Providing a balanced and nutritious feed is vital for maintaining the health and preventing diseases in your chicken flock. A high-quality feed formulated specifically for poultry provides the necessary nutrients and energy to support optimal growth and immune function. It is important to ensure that the feed contains the right balance of proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals for the specific needs of the birds. Regularly check the feed for freshness and avoid feeding moldy or spoiled feed, as they can cause digestive issues and compromise the birds’ immune system.
Clean Water Supply
Access to clean and fresh water is essential for the overall health and well-being of your chicken flock. Ensure that the water supply is clean, free from contaminants, and easily accessible to the birds at all times. Regularly clean and disinfect waterers to prevent the buildup of algae, bacteria, and other pathogens. Consider using automatic watering systems or nipple drinkers that minimize the risk of contamination. Monitor water consumption and ensure an adequate supply to prevent dehydration, as proper hydration plays a crucial role in maintaining the birds’ immune system and preventing diseases.
Housing and Ventilation
Adequate Space
Providing adequate space for your chicken flock is crucial for their health and disease prevention. Overcrowding the birds can lead to stress, increased disease transmission, and reduced overall flock health. Ensure that the coop and outdoor space allow sufficient room for the birds to move, exercise, and exhibit natural behaviors. Provide enough perches and nesting areas, considering the number and size of the birds in your flock. By allowing proper spacing, you minimize the risk of diseases spreading through direct contact and ensure better overall flock health.
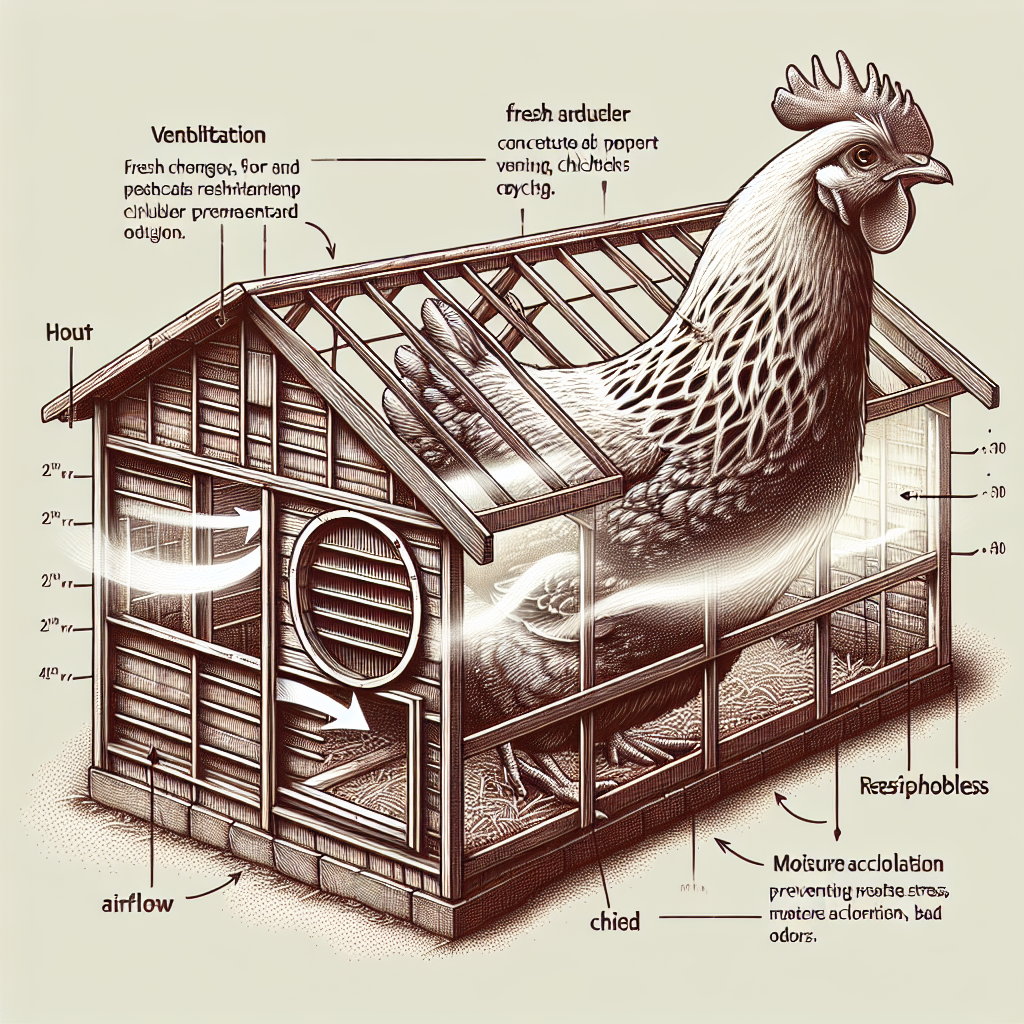
Proper Ventilation
Proper ventilation is essential in preventing diseases in a chicken flock. Good airflow helps remove moisture, ammonia, and airborne pathogens, maintaining a healthier environment for the birds. Properly designed ventilation systems ensure that the coop has sufficient fresh air exchange without causing drafts or temperature extremes. Adequate ventilation also helps control humidity levels, reducing the risk of respiratory issues and mold growth. Regularly inspect the coop for any ventilation issues and make necessary adjustments or repairs to ensure optimal air circulation.
Temperature Control
Maintaining appropriate temperatures within the chicken coop is crucial for the birds’ health and well-being. Extreme temperatures, whether too hot or too cold, can compromise the birds’ immune system and make them more susceptible to diseases. Provide sufficient insulation and ventilation to prevent temperature fluctuations. In cold weather, consider using heaters or heat lamps to maintain a comfortable temperature range, ensuring the birds stay warm and healthy. Conversely, in hot weather, provide shade, adequate airflow, and access to cool water to prevent heat stress.
Disease Monitoring
Regular Health Checks
Regularly monitoring the health of your chicken flock is essential for early disease detection and intervention. Conduct routine health checks on individual birds to assess their overall condition, behavior, and appearance. Look for any signs of illness, such as lethargy, loss of appetite, changes in feces or respiratory sounds, or abnormal feather appearance. Early detection allows for prompt treatment and isolation of sick birds, minimizing the risk of diseases spreading to the rest of the flock. Establish a consistent monitoring schedule and maintain detailed records of any observed health issues.
Observing Behavior and Symptoms
In addition to regular health checks, closely observing the behavior and symptoms of your chicken flock is crucial for disease prevention. Spend time watching the birds’ interactions, feeding habits, vocalizations, and overall activity levels. Changes in behavior, such as aggression, excessive pecking, or feather-pulling, can be indications of stress or underlying health problems. Pay attention to any abnormal symptoms, such as coughing, sneezing, wheezing, nasal discharge, or diarrhea. Promptly address any concerning behavior or symptoms and consult a veterinarian if needed.
Parasite Control
Regular Parasite Prevention Program
Implementing a regular parasite prevention program is necessary to keep your chicken flock healthy and disease-free. External parasites, such as mites and lice, can cause discomfort, skin irritations, and transmit diseases. Internal parasites, such as worms, can negatively impact the birds’ digestion, nutrient absorption, and overall health. Consult with a veterinarian to develop an appropriate parasite prevention program based on your flock’s specific needs and regional parasite risks. Regularly treat the birds with appropriate antiparasitic medications, follow recommended dosage instructions, and periodically test for parasites to ensure effectiveness.
Controlling External Parasites
Controlling and preventing external parasites is an important aspect of disease prevention in a chicken flock. Regularly inspect the birds’ feathers, skin, and legs for any signs of infestation, such as redness, irritation, or visible parasites. Treat affected birds promptly with appropriate antiparasitic products recommended by a veterinarian. Consider providing dust baths or using diatomaceous earth, a natural pest control method, to deter and control external parasites. Regularly clean and treat the coop and nesting areas to minimize the risk of infestation from the environment.
Managing Internal Parasite Infestations
Internal parasite infestations can negatively impact the health and productivity of your chicken flock. Regular monitoring and appropriate management of internal parasites are essential to prevent diseases. Conduct routine fecal examinations to detect the presence of worms or other internal parasites. Consult with a veterinarian to determine the appropriate deworming schedule and medication for your flock. Follow the recommended dosage and administration instructions to effectively control internal parasites. Proper hygiene practices, such as regularly cleaning and rotating grazing areas, can also help reduce the risk of reinfection.
Bioexclusion
Limit Poultry Contact
Limiting contact between your chicken flock and other poultry is important for preventing the spread of diseases. Avoid introducing new birds from unknown sources without appropriate quarantine and health checks. Minimize interactions between your flock and wild birds, as they can carry diseases. If you have multiple flocks, avoid mixing them unless necessary, as it increases the risk of disease transmission. Implement strict biosecurity measures, such as disinfecting equipment and footwear when moving between flocks, to prevent cross-contamination.
Isolation of Sick Birds
Isolating sick birds from the rest of the flock is essential to prevent the spread of diseases. As soon as you notice any signs of illness or abnormal behavior in a bird, promptly remove it from the main flock and place it in a separate, well-ventilated, and clean isolation area. Isolated birds should have their own feeding and drinking equipment to minimize the risk of disease transmission. Consult a veterinarian for appropriate treatment and proper isolation period to prevent the spread of diseases within the flock.
Proper Manure Management
Regular Removal of Manure
Proper manure management is crucial for maintaining a healthy and disease-free chicken flock. Regularly removing manure from the coop and surrounding areas helps minimize the buildup of harmful pathogens and reduces the risk of disease transmission. Manure should be collected and disposed of in a safe manner, following local regulations and guidelines. Consider composting manure to further reduce pathogens and create a nutrient-rich material for use in gardening or agriculture. Implementing a systematic manure removal schedule ensures a clean and healthy environment for your birds.
Safe Disposal
Proper disposal of manure is essential to prevent environmental contamination and potential disease transmission. If composting manure, ensure that the composting process reaches temperatures high enough to kill pathogens effectively. Follow local regulations and guidelines for composting or other disposal methods. Avoid spreading fresh manure near water sources, neighboring properties, or areas where the birds forage. Proper disposal not only prevents disease transmission but also promotes environmental sustainability and responsible flock management.
Health Record Keeping
Maintaining Health Records
Maintaining detailed health records is crucial for effective disease prevention and overall flock management. Keep a record of all relevant information, including vaccination dates and types, deworming schedules, health check results, and any observed abnormalities or treatments. Accurate health records allow for better disease tracking, timely interventions, and improved decision-making regarding flock management practices. Regularly update the health records and store them in a secure and easily accessible location for reference and future analysis.
Tracking Vaccinations and Treatments
Keeping track of vaccinations and treatments administered to your chicken flock is essential for disease prevention. Maintain a comprehensive record of each bird’s vaccination history, including the type of vaccine, date of administration, and any booster shots given. This information helps ensure that each bird receives the appropriate vaccinations on schedule. Similarly, record any treatments or medications administered to individual birds, including dosage, duration, and purpose. Tracking vaccinations and treatments allows for effective disease prevention and helps identify any potential gaps or issues in the flock’s health management.
Education and Training
Educating Staff on Biosecurity Measures
Educating all staff members involved in the care of your chicken flock on proper biosecurity measures is crucial for preventing disease outbreaks. Train them on the importance of hygiene practices, such as handwashing and the use of personal protective equipment. Teach them how to recognize signs of illness or abnormal behavior in the birds and instruct them on the necessary steps to take in such cases. Regularly update your staff on the latest biosecurity protocols and practices to ensure an informed and vigilant team.
Training on Disease Identification and Management
Providing training to your staff on disease identification and management is essential for effective disease prevention in your chicken flock. Teach them how to identify common diseases, their symptoms, and appropriate actions to take when a disease is suspected. Educate them on proper isolation procedures for sick birds, including handling and disposal of infected materials. Additionally, provide training on preventive measures, such as cleaning and disinfection protocols, vaccination procedures, and proper feeding and watering practices. Well-trained staff members play a vital role in maintaining a healthy and disease-free chicken flock.
By following these best practices for preventing diseases in a chicken flock, you can ensure the health and well-being of your birds. Implementing proper biosecurity measures, vaccination protocols, nutrition and hydration practices, housing and ventilation standards, disease monitoring techniques, parasite control strategies, bioexclusion protocols, manure management systems, health record keeping, and staff education and training contribute to a robust disease prevention program. With these comprehensive measures in place, you can minimize the risk of diseases and enjoy a thriving and productive chicken flock.