If you’re a proud chicken owner, ensuring the health and well-being of your flock is undoubtedly a top priority. Vaccinating your chickens serves as a crucial preventative measure against various diseases and can ultimately help maintain a thriving and disease-free environment. In this article, we will explore the best practices for vaccinating your chickens, offering valuable insights and tips to keep your feathered friends healthy and happy. So, whether you’re a seasoned poultry enthusiast or new to the world of chicken keeping, read on to discover how you can optimize the vaccination process for your beloved flock.
Vaccines for Chickens
Keeping your chickens healthy and protected from common diseases is essential for their well-being and productivity. One of the most effective ways to ensure their health is through vaccination. Vaccines stimulate the chicken’s immune system to produce antibodies that can fight off specific diseases, providing them with the necessary protection. In this article, we will guide you through the best practices for vaccinating your chickens, from choosing the right vaccines to monitoring their health after vaccination.
Choosing the Right Vaccines
Understanding the Common Diseases
Before selecting vaccines for your chickens, it is crucial to have a thorough understanding of the common diseases they are susceptible to. Diseases like Newcastle disease, infectious bronchitis, and Marek’s disease can have devastating effects on your flock if left untreated. Consult with a Poultry Veterinarian or do thorough research to familiarize yourself with the diseases prevalent in your area and the vaccines available.
Consulting a Poultry Veterinarian
It is always recommended to seek guidance from a Poultry Veterinarian when selecting vaccines for your chickens. They have the expertise and knowledge to analyze the specific needs of your flock and recommend the most suitable vaccines. A Poultry Veterinarian can also provide valuable advice on vaccination schedules and potential challenges you may encounter.
Matching Vaccines to Your Chicken’s Needs
Not all chickens require the same vaccines. Factors like breed, age, and local disease prevalence should be considered when selecting vaccines. For example, if your chickens are kept in an area with a high incidence of Marek’s disease, vaccinating against this specific disease becomes a priority. Tailor your vaccination plan to meet the individual needs of your chickens to ensure they receive the appropriate protection.
Vaccination Schedule
Determining the Appropriate Age
Determining the appropriate age for vaccination depends on the disease and the vaccine being administered. Some vaccines can be given to the chicks shortly after hatching, while others require the chickens to reach a certain age. Consult with your Poultry Veterinarian or read the vaccine manufacturer’s instructions to determine the ideal age for administering each vaccine. Ensuring the vaccines are given at the right time is vital for their effectiveness.
Considering the Disease Prevalence
The prevalence of certain diseases in your area should also influence your vaccination schedule. If a particular disease is widespread and poses a significant threat to the health of your chickens, you might need to vaccinate more frequently or develop a specific vaccination plan. Regularly monitor disease outbreaks and adjust your vaccination schedule accordingly to protect your flock.
Staggering Vaccinations
Staggering vaccinations involves administering different vaccines at different times, reducing the chance of overwhelming the chicken’s immune system. By staggering vaccinations, you allow the chickens’ immune systems to respond adequately to each vaccine, maximizing their protection. Your Poultry Veterinarian can assist in determining the optimal timing and order of vaccinations for your specific circumstances.
Preparing for Vaccination
Maintaining Proper Hygiene
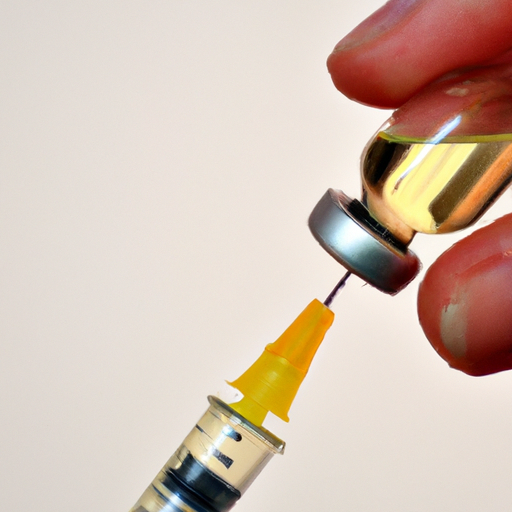
Maintaining proper hygiene is crucial when preparing for vaccination. Make sure to clean and disinfect any equipment used during the vaccination process, including syringes and needles. Sanitizing the vaccination area and washing your hands thoroughly will minimize the risk of introducing bacteria or viruses into the chickens’ bodies.
Proper Vaccine Storage and Handling
Vaccines are fragile biological products and can lose their effectiveness if not stored and handled correctly. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions regarding storage temperature, light exposure, and expiration dates. Always keep vaccines in a refrigerator specifically designated for this purpose. It is important to note that freezing vaccines can render them useless, so be cautious when storing them.
Checking Expiration Dates
Before administering any vaccine, always check the expiration date. Expired vaccines may not provide the necessary protection or could even have a detrimental effect on your chickens’ health. Remember to rotate your vaccine stock regularly, using the oldest vaccines first to ensure their potency.
The Vaccination Process
Administering Vaccines
Administering vaccines to chickens can be done through various methods, including drinking water, aerosol sprays, or injections. The chosen administration method depends on the vaccine and its mode of action. Consult with your Poultry Veterinarian to determine the most effective and appropriate method for each vaccine. Remember to handle the chickens with care and minimize stress during the vaccination process.
Choosing the Right Injection Site
If vaccinations are administered through injections, it is crucial to choose the correct injection site. The recommended site is usually the subcutaneous area, right under the skin on the back of the neck. Avoid injecting vaccines into the breast muscles, as this can result in meat condemnation if the birds are later consumed.
Proper Dosage and Mixing
Ensure that you administer the correct dosage of each vaccine as specified by the manufacturer. Underdosing can result in ineffective protection, while overdosing can have adverse effects on the chickens’ health. Follow the recommended instructions carefully and, if necessary, seek advice from your Poultry Veterinarian. For vaccines that require reconstitution, mix them thoroughly and use them promptly according to the instructions provided.
Recording Vaccinations
Maintaining accurate and up-to-date vaccination records is essential for proper flock management. Record the date, vaccine type, dosage, and any other relevant information for each vaccination given. This information will help you track the vaccination history of your chickens, identify any gaps or potential revaccination needs, and provide valuable information to your Poultry Veterinarian when seeking advice or assistance.
Monitoring after Vaccination
Observing for Adverse Reactions
After administering vaccines, it is crucial to closely monitor your chickens for any adverse reactions. Symptoms such as swelling, rashes, or behavioral changes could indicate an allergic reaction or potential vaccine failure. If you notice any concerning signs, contact your Poultry Veterinarian immediately for guidance and evaluation.
Post-Vaccination Care
Post-vaccination care involves creating a stress-free environment for your chickens to boost their immune response. Provide access to clean water, nutritious feed, and comfortable housing. Minimize stress factors such as overcrowding, harsh weather conditions, or sudden changes in the coop environment. A healthy and stress-free environment will support the chickens’ immune systems, ensuring the effectiveness of the vaccines.
Maintaining a Healthy Environment
Biosecurity Measures
Implementing proper biosecurity measures is essential to prevent the introduction and spread of diseases within your flock. This involves practicing good hygiene, limiting contact with other chickens or wild birds, and controlling pests. Regularly clean and disinfect your chicken coops, equipment, and footwear to minimize the risk of disease transmission. Additionally, consider implementing strict visitor protocols and quarantine procedures for new birds to safeguard the health of your flock.
Disease Prevention Strategies
Vaccination is just one aspect of maintaining the health of your chickens. Implementing disease prevention strategies is equally important. This includes keeping a clean and well-ventilated coop, providing a balanced diet, and regularly inspecting your chickens for signs of disease. Additionally, avoid introducing new birds without proper quarantine and testing procedures to prevent the introduction of new diseases to your flock.
Vaccination Revaccination
Determining the Need for Revaccination
Some vaccines require revaccination to maintain continuous protection against specific diseases. Determining the need for revaccination depends on various factors such as disease prevalence, vaccine efficacy, and the specific vaccine used. Consult with your Poultry Veterinarian to establish an appropriate revaccination schedule tailored to your flock’s needs.
Interval between Vaccination and Revaccination
The interval between vaccination and revaccination varies depending on the vaccine, disease, and prevailing conditions. Some vaccines may require annual revaccination, while others may have a longer duration of immunity. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations and the advice of your Poultry Veterinarian to ensure your chickens receive timely revaccination to maintain their protection.
Vaccination Challenges and Limitations
Potential Vaccine Failures
Although vaccination is highly effective, there is a small chance of vaccine failure. Factors such as improper storage or handling, administration errors, or the presence of maternal antibodies can hinder the vaccine’s efficacy. Monitoring for any signs of disease and regular communication with your Poultry Veterinarian are essential to address any potential vaccine failures promptly.
Vaccine Interference
Some vaccines may interfere with each other’s efficacy if administered simultaneously. It is crucial to consult with your Poultry Veterinarian to develop a vaccination plan that minimizes any potential interference. They can guide you on the optimal timing and sequence of vaccinations to ensure maximum effectiveness.
By following the best practices outlined in this article, you will be well-equipped to protect the health of your chickens through proper vaccination. Remember, consulting with a Poultry Veterinarian and maintaining a healthy environment are key components of a successful vaccination program. Taking these precautions not only promotes the well-being of your flock but also contributes to the overall productivity and happiness of your chickens.